I'm not the greatest public speaker and sometimes it is very difficult for me to stay calm, kool, and collected when its my Neighbors who are suffering. I hope I made it clear:
To me that makes me think:
1) They are instructed to Lie.
2) They are being fed "misinformation".
3) They honestly don't know.
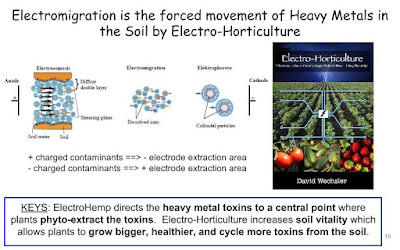
- We can fix everyone yards but unless they stop the radiation at the source it will continue to spread toxins.
- With the Teams new findings I believe we are going to be able to detoxify 6 to 8 yards at one time. If done as a DIY neighborhood project the costs will be affordable. But before we get too excited about this. I have a meeting coming up on Mar 31st to talk with the Team's Nuclear Adviser who is in town. During this meeting we will discuss how best it will be to instruct a community how to save themselves. Nobody else is going to help. We are going to have to save ourselves.
- Repoint out: We will be able to detoxify the entire yard at one time.
- Vote for the Science behind: ElectroHemp BioRad Organic Disposal
In the case of 2 and 3 above points to a severe lack of Interagency Communications. And since this is a Superfund hazardous waste site that falls under EPA, EM, CERCLA rules and doesn't one time mention FUSRAP who have shown "offsite" contamination. How can one Government Entity not inform the other guys working down the street? Is our Government that dysfunctional that with such a widespread contamination event- they choose "not to work together" or with other Government Entities?
The First photo is a diagram example of a low cost option of using a fenced in area to grow the phytoremediation plants.
Using the same design with a
Greenhouse or Hoophouse will allow a greater variety of phytoremediation plants to be grown year round.
Inside the Green House will be an area that will be used to hold the disposal tanks.
This is the area where the plants that cycled the toxins from the ground> into the plant> and then into the disposal tanks> that will turn the toxins inert> while generating electricity.
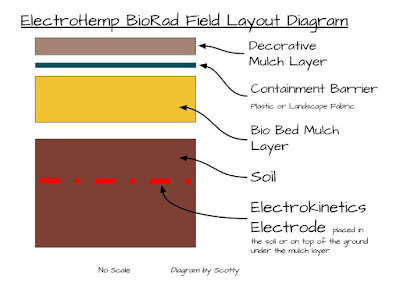
ElectroHemp BioRad Hazardous Waste Multi Yard Treatment
Example of a Randomly picked neighborhood with the 1 mile contamination zone around the Westlake Landfill updated July 5, 2016