- Phytoextraction of As and Fe using Hibiscus cannabinus L. from soil polluted with landfill leachate.Int J Phytoremediation. 2012 Feb;14(2):186-99. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2011.587481.PMID: 22567704
- Effects of peat on plant growth and lead and zinc phytostabilization from lead-zinc mine tailing in southern China: Screening plant species resisting and accumulating metals.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019 Jul 30;176:42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.078. Epub 2019 Mar 25.PMID: 30921695
- Potential of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) and corn (Zea mays L.) for phytoremediation of dredging sludge contaminated by trace metals.Biodegradation. 2013 Jul;24(4):563-7. doi: 10.1007/s10532-013-9626-5. Epub 2013 Feb 23.PMID: 23436151
- Ascorbate-Glutathione Cycle and Ultrastructural Analyses of Two Kenaf Cultivars (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) under Chromium Stress.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Jul 11;15(7):1467. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15071467.PMID: 29997377 Free PMC article.
- Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) Seed and its Potential Food Applications: A Review.J Food Sci. 2019 Aug;84(8):2015-2023. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14714. Epub 2019 Jul 30.PMID: 31364175 Review.
- [Using kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) to reclaim multi-metal contaminated acidic soil].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2013 Mar;24(3):832-8.PMID: 23755502 Chinese.
- Nitrogen dioxide at an ambient level improves the capability of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) to decontaminate cadmium.Int J Phytoremediation. 2008 Jan-Feb;10(1):73-6. doi: 10.1080/15226510701827085.PMID: 18709933
- Phytotreatment of soil contaminated with used lubricating oil using Hibiscus cannabinus.Biodegradation. 2012 Apr;23(2):277-86. doi: 10.1007/s10532-011-9506-9. Epub 2011 Aug 26.PMID: 21870160
- Potential of Sonchus arvensis for the phytoremediation of lead-contaminated soil.Int J Phytoremediation. 2008 Jul-Aug;10:325-42. doi: 10.1080/15226510802096184.PMID: 19260217
- Physiological responses and tolerance of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) exposed to chromium.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2016 Nov;133:509-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.08.007. Epub 2016 Aug 21.PMID: 27553521
- Morpho-physiological traits, biochemical response and phytoextraction potential of short-term copper stress on kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) seedlings.PeerJ. 2020 Jan 30;8:e8321. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8321. eCollection 2020.PMID: 32030320 Free PMC article.
- Phytoremediation of lead (Pb) and arsenic (As) by Melastoma malabathricum L. from contaminated soil in separate exposure.Int J Phytoremediation. 2014;16(7-12):694-703. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2013.856843.PMID: 24933879
- Growth and lead accumulation by the grasses Vetiveria zizanioides and Thysanolaena maxima in lead-contaminated soil amended with pig manure and fertilizer: a glasshouse study.Chemosphere. 2007 Jan;66(1):45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.05.038. Epub 2006 Jul 10.PMID: 16828842
- Phytostabilization of a Pb-contaminated mine tailing by various tree species in pot and field trial experiments.Int J Phytoremediation. 2012 Oct;14(9):925-38. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2011.636403.PMID: 22908655
- Role of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on lead uptake and translocation by tumbleweed (salsola kali L.).Environ Toxicol Chem. 2007 May;26(5):1033-9. doi: 10.1897/06-239r.1.PMID: 17521152
- Bioremediation of industrially contaminated soil using compost and plant technology.J Hazard Mater. 2016 Mar 5;304:166-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.10.061. Epub 2015 Oct 30.PMID: 26551220
- Effect of Emulsification Method and Particle Size on the Rate of in vivo Oral Bioavailability of Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) Seed Oil.J Food Sci. 2018 Jul;83(7):1964-1969. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14191. Epub 2018 May 26.PMID: 29802733
- Phytoremediation of wastewater containing lead (Pb) in pilot reed bed using Scirpus grossus.Int J Phytoremediation. 2013;15(7):663-76. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2012.723069.PMID: 23819266
- Phytoextraction of Pb and Cd by the Mediterranean saltbush (Atriplex halimus L.): metal uptake in relation to salinity.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2009 Nov;16(7):844-54. doi: 10.1007/s11356-009-0224-3. Epub 2009 Jul 14.PMID: 19597858
- Lead accumulation, growth responses and biochemical changes of three plant species exposed to soil amended with different concentrations of lead nitrate.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019 Apr 30;171:26-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.058. Epub 2018 Dec 27.PMID: 30594754
Organic Remediation and Toxic Cleanup Its Not Rocket Science - Its Phyto Science. The magic happens in the roots of the plants Naturally with Phytoremediation
Showing posts with label Kenaf. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Kenaf. Show all posts
Saturday, September 26, 2020
Kenaf Hibiscus Cannabinus L for Phytoremediation -Science Studies-
Wednesday, August 31, 2016
IKEAs lesser known environmental project
If only more business cared about the environment as much as IKEA does.
Most everyone has heard that the St Louis IKEA Store is powered by solar panels! Here is a lesser known environmental project they have incorporated into the property along Forest Park and Vandeventer Streets.
The parking lot in of the St Louis IKEA store drains into a low $$$ cost natural phytoremediation filter system.
Article 1 Plants as Water Protectors blog series
Article 5- Phytromediation Rafts with Electrokinetics
Article 4- Plants as Water Protectors
Article 2- St Louis IKEA Phyto Buffer Zone pt2
Article 1- IKEAs lesser known environmental project
The IKEA's Engineers and Crew that installed the water filtration Phytoremediation project did a seamless job of blending the bioremediation system into the natural environment. If it wouldn't have been for my growing the Kenaf plants and seeing the unmistakable Kenaf Flowers- I may not have noticed.
 |
| IKEA Parking Lot drains away from the building into modified riparian buffers along Forest Park Parkway and Vandeventer |
 |
| Any contaminants that escape or drip from the Autos in the parking lot will eventually make their way into the modified riparian buffer zone that removes the toxins naturally |
 |
| The break in the concrete curb allows the water to enter the riparian buffer zone where the Plants naturally cycle the toxins from the water. |
 |
| Phytoremediation Plants are growing in a bed of Gravel and Rock allowing the roots of the plants direct contact with the toxins that will be removed by Phytoremediation. |
 |
Toxins and Contaminants are removed the Natural Way by using Plants in a process called Phytoremediation.https://electrohemp.blogspot.com/2017/07/citizen-science-phytoremediation.html |
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Search This Blog
ElectroHemp Introduction
ElectroHemp Hazardous Waste Remediation Intro
ElectroHemp BioRad Hazardous Waste Cleanup Introduction ElectroHemp - BioRad CleanUp 5 Stage Phytoremediation Treatment Train - Remove...
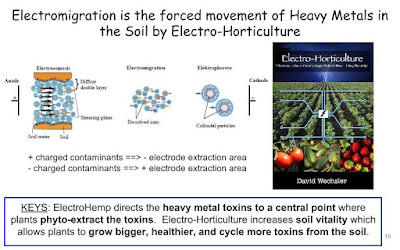
-
while reading this I realized the EPA are addressing the spread of the toxins but not the cause of the toxins. tsk tsk tsk @EPA Are you s...
-
If only more business cared about the environment as much as IKEA does. Most everyone has heard that the St Louis IKEA Store is powered ...
-
ElectroHemp BioRad Hazardous Waste Cleanup Introduction ElectroHemp - BioRad CleanUp 5 Stage Phytoremediation Treatment Train - Remove...







