- Phytoextraction of As and Fe using Hibiscus cannabinus L. from soil polluted with landfill leachate.Int J Phytoremediation. 2012 Feb;14(2):186-99. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2011.587481.PMID: 22567704
- Effects of peat on plant growth and lead and zinc phytostabilization from lead-zinc mine tailing in southern China: Screening plant species resisting and accumulating metals.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019 Jul 30;176:42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.078. Epub 2019 Mar 25.PMID: 30921695
- Potential of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) and corn (Zea mays L.) for phytoremediation of dredging sludge contaminated by trace metals.Biodegradation. 2013 Jul;24(4):563-7. doi: 10.1007/s10532-013-9626-5. Epub 2013 Feb 23.PMID: 23436151
- Ascorbate-Glutathione Cycle and Ultrastructural Analyses of Two Kenaf Cultivars (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) under Chromium Stress.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Jul 11;15(7):1467. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15071467.PMID: 29997377 Free PMC article.
- Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) Seed and its Potential Food Applications: A Review.J Food Sci. 2019 Aug;84(8):2015-2023. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14714. Epub 2019 Jul 30.PMID: 31364175 Review.
- [Using kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) to reclaim multi-metal contaminated acidic soil].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2013 Mar;24(3):832-8.PMID: 23755502 Chinese.
- Nitrogen dioxide at an ambient level improves the capability of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) to decontaminate cadmium.Int J Phytoremediation. 2008 Jan-Feb;10(1):73-6. doi: 10.1080/15226510701827085.PMID: 18709933
- Phytotreatment of soil contaminated with used lubricating oil using Hibiscus cannabinus.Biodegradation. 2012 Apr;23(2):277-86. doi: 10.1007/s10532-011-9506-9. Epub 2011 Aug 26.PMID: 21870160
- Potential of Sonchus arvensis for the phytoremediation of lead-contaminated soil.Int J Phytoremediation. 2008 Jul-Aug;10:325-42. doi: 10.1080/15226510802096184.PMID: 19260217
- Physiological responses and tolerance of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) exposed to chromium.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2016 Nov;133:509-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.08.007. Epub 2016 Aug 21.PMID: 27553521
- Morpho-physiological traits, biochemical response and phytoextraction potential of short-term copper stress on kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) seedlings.PeerJ. 2020 Jan 30;8:e8321. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8321. eCollection 2020.PMID: 32030320 Free PMC article.
- Phytoremediation of lead (Pb) and arsenic (As) by Melastoma malabathricum L. from contaminated soil in separate exposure.Int J Phytoremediation. 2014;16(7-12):694-703. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2013.856843.PMID: 24933879
- Growth and lead accumulation by the grasses Vetiveria zizanioides and Thysanolaena maxima in lead-contaminated soil amended with pig manure and fertilizer: a glasshouse study.Chemosphere. 2007 Jan;66(1):45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.05.038. Epub 2006 Jul 10.PMID: 16828842
- Phytostabilization of a Pb-contaminated mine tailing by various tree species in pot and field trial experiments.Int J Phytoremediation. 2012 Oct;14(9):925-38. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2011.636403.PMID: 22908655
- Role of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on lead uptake and translocation by tumbleweed (salsola kali L.).Environ Toxicol Chem. 2007 May;26(5):1033-9. doi: 10.1897/06-239r.1.PMID: 17521152
- Bioremediation of industrially contaminated soil using compost and plant technology.J Hazard Mater. 2016 Mar 5;304:166-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.10.061. Epub 2015 Oct 30.PMID: 26551220
- Effect of Emulsification Method and Particle Size on the Rate of in vivo Oral Bioavailability of Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) Seed Oil.J Food Sci. 2018 Jul;83(7):1964-1969. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14191. Epub 2018 May 26.PMID: 29802733
- Phytoremediation of wastewater containing lead (Pb) in pilot reed bed using Scirpus grossus.Int J Phytoremediation. 2013;15(7):663-76. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2012.723069.PMID: 23819266
- Phytoextraction of Pb and Cd by the Mediterranean saltbush (Atriplex halimus L.): metal uptake in relation to salinity.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2009 Nov;16(7):844-54. doi: 10.1007/s11356-009-0224-3. Epub 2009 Jul 14.PMID: 19597858
- Lead accumulation, growth responses and biochemical changes of three plant species exposed to soil amended with different concentrations of lead nitrate.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019 Apr 30;171:26-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.058. Epub 2018 Dec 27.PMID: 30594754
Organic Remediation and Toxic Cleanup Its Not Rocket Science - Its Phyto Science. The magic happens in the roots of the plants Naturally with Phytoremediation
Saturday, September 26, 2020
Kenaf Hibiscus Cannabinus L for Phytoremediation -Science Studies-
Tuesday, January 15, 2019
An Asian grass can be the key to removing lead from contaminated soil
 |
| Sewan grass (Lasiurus scindicus Henrard) is a perennial grass that can live up to 20 years. It is a bushy, multi-branched desert grass with ascending to erect wiry stems, up to a height of 1-1.6 m, and a stout woody rhizome (FAO, 2010; Ecocrop, 2010). Leaves are alternate with a thin leaf-blade. The inflorescence is a silky, 10 cm long raceme bearing hairy spikelets. The fruit is a caryopsis (Anon., 2010; eFloras, 2010; FAO, 2010; Burkill, 1985). Sewan grass forms bushy thickets in sandy deserts where it is used for pasture, hay and fodder for livestock. This grazing pasture is of outmost importance in areas where annual rainfall is below 250 mm (Ecocrop, 2010). It is relished by ruminants but does not stand heavy grazing and disappears when overgrazed (El-Keblawy et al., 2009). |
Research from JECRC University in India is no exception, as they found a process which restores soil that has been polluted with lead. The study, published in the American […] For the study, researchers utilized phytoremediation to remove the lead from contaminated soil.
Defined as “the efficient use of plants to remove, detoxify or immobilize environmental contaminants in a growth matrix (soil, water or sediments) through the natural biological, chemical or physical activities and processes of the plant,” the procedure refers to a number of technologies that use plants to remove both organic and inorganic contaminants in soil and water.
In this procedure, plants are grown in polluted soil to either remove a contaminant, contain it in their roots, or even degrade it completely. These plants are then harvested, processed, and disposed of.
The team first collected soil and water samples that have been contaminated by lead and put these in pots in differing concentrations. They then sowed sewan grass over a 105-day pot trial period. During this time, the team regularly sampled the soil and water to evaluate the amount of heavy metal was present in the soil.
Based on the findings, the researchers discovered that lead adversely affected the growth of sewan grass from the experiment. However, they also found that it was receptive to the lead and that the roots had accumulated it. During the samples, they found increased concentrations of lead in the roots on the 45th and 65th day after exposure.
“The lead accumulation in Lasiurus scindicus (mostly in its roots) confirming its potentiality as a phytoremediator and due to polluted soil pH high amount of lead accumulated in root compare to [the leaves],” the researchers concluded. They also looked at the potential of the grass to be further developed to restore lead-polluted soil.
Friday, December 28, 2018
Phytoremediation Alligator Weed Lead + Mercury
 |
| Phytoremediation with Alligator Weed to remove Lead and Mercury from water. |
Alternanthera philoxeroides, commonly referred to as alligator weed, is a native species to the temperate regions of South America, which includes Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay. Argentina alone, hosts around 27 species that fall within the range of the genus Alternanthera. Wikipedia
Article Science paper: Metal hyperaccumulation in plants - Biodiversity prospecting for phytoremediation technologys source Edible plants and vegetables crops plants and vegetables crops
The dominant leaf vegetable producing species viz. Amaranthus spinosus, Alternanthera philoxeroides and A. sessiles growing on the sewage sludge of Musi river located in greater Hyderabad City (close to 17º26' N latitude and 78º27' E longitude), Andhra Pradesh, India was investigated for metal accumulation.
- The transfer factor for metals was calculated Metal content in plant part (dry wt.)/ Metal content in soil (dry.wt).
- Transfer factor and metal content Cd (non-essential), Zn and Fe (essential) in plant parts of these selected species indicate their aility to bioconcentrate in their tissues (Figure 12).
- The concentration of these metals is invariably high in leaf tissue (Bañuelos and Meek, 1989; Prasad, 2001b).
- Thus, it is possible to use these species to restore the biosolid and sewage sludge contaminated sites, while exercising caution on human consumption.
It is also possible to supplement the dietary requirement of human food with Zn and Fe as these being essential nutrients and the plant species are edible.
[Warning] However, there is a need to monitor the metal transfer factor through food chain (Bañuelos and Meek, 1989; Bañuelos et al. 1993a; Bañuelos et al. 1993b).
Alligator Weed description courtesy of Wikipedia- Alternanthera philoxeroides can thrive in both dry and aquatic environments and is characterized by whitish, papery flowers along its short stalks, irregular, or sprawling hollow stems, and simple and opposite leave pattern sprouting from its nodes. The species is dioecious. It is also considered a herbaceous plant due to its short-lived shoot system. It produces horizontal stems, otherwise known as stolons, that can sprout up to 10 m in length and thanks to its hollow stems, floats easily. This results in large clusters of stem to amass and create dense mats along the surface. The plant flowers from December to April and usually grows around 13 mm in diameter and tend to be papery and ball-shaped. The weed's intricate root system can either allow them to hang free in the water to absorb nutrients or directly penetrate the soil/sediment and pull their nutrients from below.
Monday, August 22, 2016
The Age of Fission Lonnie Clark guest Scotty - Phytoremediation Pr...
Lonnie Clark-The Age of Fission, interviewing Scotty and
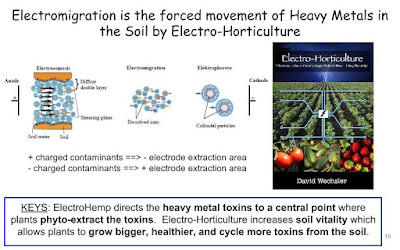
the ElectroHemp BioRad process and system that removes
heavy metal toxins organically.
Friday, June 24, 2016
ElectroHemp BioRad Disposal will work for Lead too!
The overall metal uptake in plant system was higher under EAPR system than one compared with phytoremediation process.
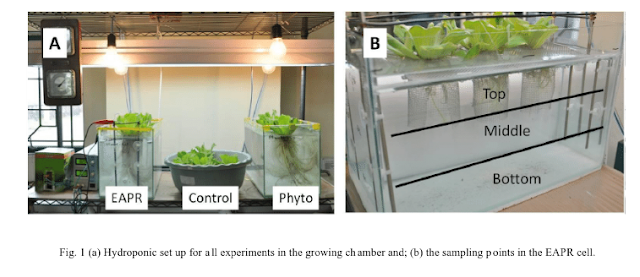 |
| Electrokinetics water lettuce phytoremediation science lab project. |
Removal of Lead and Copper from Contaminated Water Using EAPR System and Uptake by Water Lettuce (Pistia Stratiotes L.)
Search This Blog
ElectroHemp Introduction
ElectroHemp Hazardous Waste Remediation Intro
ElectroHemp BioRad Hazardous Waste Cleanup Introduction ElectroHemp - BioRad CleanUp 5 Stage Phytoremediation Treatment Train - Remove...
-
while reading this I realized the EPA are addressing the spread of the toxins but not the cause of the toxins. tsk tsk tsk @EPA Are you s...
-
If only more business cared about the environment as much as IKEA does. Most everyone has heard that the St Louis IKEA Store is powered ...
-
ElectroHemp BioRad Hazardous Waste Cleanup Introduction ElectroHemp - BioRad CleanUp 5 Stage Phytoremediation Treatment Train - Remove...









