I encourage everyone: if you don't think the creator has provided solutions to our problems, you might try getting out of the box and explore other avenues and thought patterns.
The Pollution Solution : Electricity Production by Geobacter sulfurreducen... https://t.co/xzxowpTHFz pic.twitter.com/hMZjsZ3s9X
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) January 17, 2023
i'm working a few projects, i've been waiting for an opportunity like this. i have been selecting interim crews to help serve as board members on https://t.co/McBKm8PvPy my other stuff is Farming Related and I also have a Kenya Africa project for later on down the road.
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) January 23, 2023
The Pollution Solution - https://t.co/6SGxnDqnBs
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) January 2, 2023
The Solution to Pollution https://t.co/IUKsiT2n1f
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) January 6, 2023
The Pollution Solution : The efficiency of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) in remediating sites #phytoremediation https://t.co/ir6zrge7Oy
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) January 18, 2023
Dirty Water IN Clean Water OUT. its so simple, that the brainiac scientist in charge can't get outa the box. What do environmental scientist do all day, Play Tiddlywinks? Cuz a lowly carpenter from StLouis MO figured out the solution to the worlds pollution. #CanYouHearMeNOW pic.twitter.com/4j2jf6sWDP
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) January 18, 2023
i wanna clean up the earth. > WE ARE THE POLLUTION SOLUTION
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) January 24, 2023
THE POLLUTION SOLUTION SPECIALIZES IN TECHNIQUES AND SERVICES FOR NATURALLY INSPIRED AND COST EFFECTIVE REMOVAL AND REMEDIATION OF TOXINS AND CONTAMINANTS FROM AIR, SOIL, AND WATER. https://t.co/McBKm8PvPy
.@UnitedNewsChan1
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) January 2, 2023
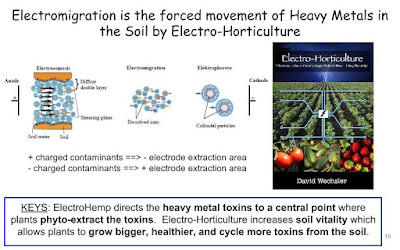
back to #ThePollutionSolution here is a slide show about how and why this natural solution can clean up any toxin or pollution. https://t.co/1Q2CGGaQh5
Electrohemp was renamed to #PollutionSolution hemp has limits this doesn't. https://t.co/McBKm8PvPy
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) January 25, 2023



.jpeg)