Dead Chickens in the Chemical Spill is a warning that our Government is ignoring.
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) February 14, 2023
If it negatively harms the environment it negatively affects people. https://t.co/Jjm8uCoRM5 pic.twitter.com/luUAdAYICa
OHIO 🚨 Woman finds all her chickens dead 10 miles from East Palestine, Ohio
#OhioTrainDisaster #OhioRiver
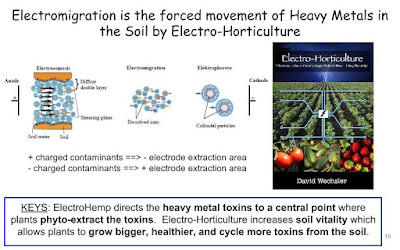
There are solutions to pollution. The Ohio Train Derailment and the toxins that are being reported on the Ohio River can be cleaned up. Here are examples of removing chemicals from water with modified hemp core.
Why is it so hard to work with the EPA? I've been trying for years? Their silence is deafening.
oil skimmers are full of hemp / kenaf core materials that soak up pollution. reports the toxins creating a rainbow on the water surface... its on top and can be removed! #ohioriver #pollution #remediation pic.twitter.com/hR8HLrlzyh
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) February 13, 2023
Water Pollution and Chemical Cleanup with Modified Hemp Core https://t.co/aKsUD5Je7g
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) February 14, 2023
I've tried for years to work with the @EPA @EPAregion7 hacks.... their silence is deafening. https://t.co/6KpnED6X3i
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) February 14, 2023
@Grow_Fruit_Fl @realstewpeters @5150TatorSala
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) February 14, 2023
Water cleanup example. Note the modified hemp absorbs only the toxins not the water. https://t.co/McBKm8OY00
Why is it so hard to work with @EPA @EPAregion7 Ive tried for years?
#HazardousWaste #Remediation #OhioChernobyl pic.twitter.com/CDRhNQXTUb
We are The Pollution Solution The Goal of the Pollution Solution is to turn toxins and contaminants into $$ cash to offset the cost of remediation of cleanup projects which will allow for future use of the property that will not pose a health danger to People, Animals, and the Ecosystem.thats a new one on me. I'll keep it in mind. Share the info if you have it. Lord knows the @EPA hacks aren't doing their jobs. #OhioChernobyl
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) February 14, 2023
Recently released bodycam footage shows Ohio reporter Evan Lambert getting arrested for doing what big media won’t:
— DC_Draino (@DC_Draino) February 13, 2023
Ask real questions about toxic chemicals poisoning people’s water and air and killing thousands of animals
Where is FEMA?!
pic.twitter.com/vnpCD9w5OC