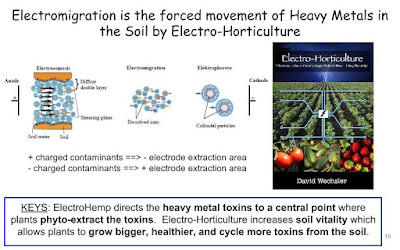
ElectroHemp is preparing for R&D Projects that will highlight how their system speeds up contamination removal and organically disposes hazardous waste.
- Phytoremediation Assisted Contamination Cleanup
- Organic Hazardous Waste Disposal
- Turning Hazardous Waste into income
- Soil and Water Buffer Zones
- Phytoremediation Rafts for water cleanup and remediation
If you or your organization would like to join in, partner, sponsor, advertise, or just learn more about the R&D projects use the contact form, subscribe to the blog feed or stay tuned by monitoring the blog.