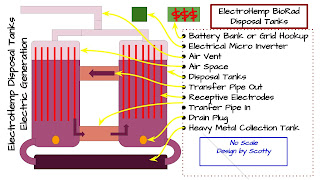
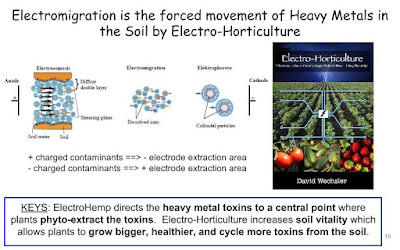
I dug out some Phytoremediation Research Articles that talk about the uptake availability of Hemp and Plants to cycle the toxins and heavy metals from the soil
Clean Up the Environment. I Raskin, ed. Wiley Interscience, John Wiley and Sons, Inc. New York, NY
- As in the case of treating heavy metals, phytoremediation has been proven to be most effective and at a more advanced stage of development for treating readily available contaminants and therefore to treat wastewater, surface water and groundwater contamination, including the hydraulic control of tritiated groundwater.
Soil-adsorbed radionuclides have been more difficult to treat, and success in soil treatment at this stage depends on the development of specific amendments and treatments that can increase the rate of transfer of the radionuclide into plant-available forms, without further dispersing radionuclides into the environment.
________
Metal hyperaccumulation in plants - Biodiversity prospecting for phytoremediation technology
Full Text http://www.ejbiotechnology.info/index.php/ejbiotechnology/article/view/v6n3-6/617
Abstract
The importance of biodiversity (below and above ground) is increasingly considered for the cleanup of the metal contaminated and polluted ecosystems. This subject is emerging as a cutting edge area of research gaining commercial significance in the contemporary field of environmental biotechnology. Several microbes, including mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal fungi, agricultural and vegetable crops, ornamentals, and wild metal hyperaccumulating plants are being tested both in lab and field conditions for decontaminating the metalliferous substrates in the environment. As on todate about 400 plants that hyperaccumulate metals are reported. The families dominating these members are Asteraceae, Brassicaceae, Caryophyllaceae, Cyperaceae, Cunouniaceae, Fabaceae, Flacourtiaceae, Lamiaceae, Poaceae, Violaceae, and Euphobiaceae. Brassicaceae had the largest number of taxa viz. 11 genera and 87 species. Different genera of Brassicaceae are known to accumulate metals. Ni hyperaccumulation is reported in 7 genera and 72 species and Zn in 3 genera and 20 species. Thlaspi species are known to hyperaccumulate more than one metal i.e. T. caerulescence = Cd, Ni. Pb, and Zn; T. goesingense = Ni and Zn and T. ochroleucum = Ni and Zn and T. rotundifolium = Ni, Pb and Zn. Plants that hyperaccumulate metals have tremendous potential for application in remediation of metals in the environment. Significant progress in phytoremediation has been made with metals and radionuclides. This process involves rising of plants hydroponically and transplanting them into metal-polluted waters where plants absorb and concentrate the metals in their roots and shoots. As they become saturated with the metal contaminants, roots or whole plants are harvested for disposal. Most researchers believe that plants for phytoremediation should accumulate metals only in the roots. Several aquatic species have the ability to remove heavy metals from water, viz., water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes(Mart.) Solms); pennywort (Hydrocotyle umbellata L.) and duckweed (Lemna minor L.). The roots of Indian mustard are effective in the removal of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn and sunflower removes Pb, U, 137Cs, and 90Sr from hydroponic solutions. Aquatic plants in freshwater, marine and estuarine systems act as receptacle for several metals. Hyperaccumulators accumulate appreciable quantities of metal in their tissue regardless of the concentration of metal in the soil, as long as the metal in question is present. The phytoextraction process involves the use of plants to facilitate the removal of metal contaminants from a soil matrix. In practice, metal-accumulating plants are seeded or transplanted into metal-polluted soil and are cultivated using established agricultural practices. If metal availability in the soil is not adequate for sufficient plant uptake, chelates or acidifying agents would be applied to liberate them into the soil solution. Use of soil amendments such as synthetics (ammonium thiocyanate) and natural zeolites have yielded promising results. Synthetic cross-linked polyacrylates, hydrogels have protected plant roots from heavy metals toxicity and prevented the entry of toxic metals into roots. After sufficient plant growth and metal accumulation, the above-ground portions of the plant are harvested and removed, resulting the permanent removal of metals from the site. Soil metals should also be bioavailable, or subject to absorption by plant roots. Chemicals that are suggested for this purpose include various acidifying agents, fertilizer salts and chelating materials. The retention of metals to soil organic matter is also weaker at low pH, resulting in more available metal in the soil solution for root absorption. It is suggested that the phytoextraction process is enhanced when metal availability to plant roots is facilitated through the addition of acidifying agents to the soil. Chelates are used to enhance the phytoextraction of a number of metal contaminants including Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn Researchers initially applied hyperaccumulators to clean metal polluted soils. Several researchers have screened fast-growing, high-biomass-accumulating plants, including agronomic crops, for their ability to tolerate and accumulate metals in their shoots. Genes responsible for metal hyperaccumulation in plant tissues have been identified and cloned. Glutathione and organic acids metabolism plays a key role in metal tolerance in plants. Glutathione is ubiquitous component cells from bacteria to plants and animals. In phytoremediation of metals in the environment, organic acids play a major role in metal tolerance. Organic acids acids form complexes with metals, a process of metal detoxification. Genetic strategies and transgenic plant and microbe production and field trials will fetch phytoremediaition field applications.The importance of biodiversity and biotechnology to remediate potentially toxic metals are discussed in this paper. Brassicaceae amenable to biotechnological improvement and phytoremediation hype are highlighted.
________
http://www.bioon.com/biology/UploadFiles/200412/20041229195615844.pdf
Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) has been used to examine its capability as a renewable resource to decontaminate heavy metal polluted soils (Linger et al. 2002). Metal accumulation in different parts of the plant was studied (i.e., seeds, leaves, fibres and hurds), and the highest concentrations of all 80 examined metals (i.e., Ni, Pb, Cd) are found in the leaves.
"Hemp shows a phytoremediation potential of 126 g Cd ha/1 vegetation per period.
________
Linger P, Mu¨ssig J, Fischer H & Kobert J (2002) Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) growing on heavy metal contaminated soil: fibre quality and phytoremediation potential. Industr. Crops Protect. 16: 33–42 See Vote Hemp - Phytoremediation with Hemp
Abstract
The effects of different cadmium concentrations [17 mg(Cd) kg-1(soil) and 72 mg(Cd) kg-1(soil)] on Cannabis sativa L. growth and photosynthesis were examined. Hemp roots showed a high tolerance to Cd, i.e. more than 800 mg(Cd) kg-1(d.m.) in roots had no major effect on hemp growth, whereas in leaves and stems concentrations of 50 - 100 mg(Cd) kg-1(d.m.) had a strong effect on plant viability and vitality. For control of heavy metal uptake and xylem loading in hemp roots, the soil pH plays a central role. Photosynthetic performance and regulation of light energy consumption were analysed using chlorophyll fluorescence analysis. Seasonal changes in photosynthetic performance were visible in control plants and plants growing on soil with 17 mg(Cd) kg-1(soil). Energy distribution in photosystem 2 is regulated in low and high energy phases that allow optimal use of light and protect photosystem 2 from overexcitation, respectively. Photosynthesis and energy dissipation were negatively influenced by 72 mg(Cd) kg-1(soil). Cd had detrimental effects on chlorophyll synthesis, water splitting apparatus, reaction centre, antenna and energy distribution of PS 2. Under moderate cadmium concentrations, i.e. 17 mg(Cd) kg-1(soil), hemp could preserve growth as well as the photosynthesis apparatus, and long-term acclimation to chronically Cd stress occurred. Additional key words: acclimation, chlorophyll fluorescence, phytoextraction, quenching, tolerance.
- Conclusion Hemp is a Cd-tolerant plant, with strong resistant roots and the capability for long-term acclimation. These characteristics endorse hemp as a key candidate for phytoextration approaches.
- For plant survival, the control of cadmium transport to stems and leaves is highly critical.
- When Cd concentrations in leaves exceed a threshold, PS 2 is influenced in a complex manner, chlorophyll synthesis, water splitting, Calvin cycle enzymes and regulation of energy distribution of PS 2 are effected.
______________
Phytoremediation of heavy metals: Recent techniques Chhotu D. Jadia and M. H. Fulekar* Environmental Biotechnology Laboratory, Department of Life Sciences, University of Mumbai, Santacruz (E), Mumbai - 400 098, India. Accepted 19 December, 2008 http://www.ajol.info/index.php/ajb/article/viewFile/59987/48257
CONCLUSION
The pollution of soil and water with heavy metals is an environmental concern today. Metals and other inorganic contaminants are among the most prevalent forms of contamination found at waste sites, and their remediation in soils and sediments are among the most technically difficult. The high cost of existing cleanup technologies led to the search for new cleanup strategies that have the potential to be low-cost, low-impact, visually benign, and environmentally sound. Phytoremediation is a new cleanup concept that involves the use of plants to clean or stabilize contaminated environments. Phytoremediation is a potential remediation strategy that can be used to decontaminate soils contaminated with inorganic pollutants. Research related to this relatively new technology needs to be promoted and emphasized and expanded in developing countries since it is low cost. In situ, solar driven technology makes use of vascular plants to accumulate and translocate metals from roots to shoots. Harvesting the plant shoots can permanently remove these contaminants from the soil. Phytoremediation does not have the destructive impact on soil fertility and structure that some more vigorous conventional technologies have such as acid extraction and soil washing. This technology can be applied “in situ” to remediate shallow soil, ground water and surface water bodies. Also, phytoremediation has been perceived to be a more environmentally-friendly “green” and lowtech alternative to more active and intrusive remedial methods.
MOhemp Energy: Hazardous Waste Escapes in Flood: The Bridgeton and Westlake Landfills have flooded and the toxins are escaping, a perfect example of places that natural Phytoremediat...