DO YOU TRUST GOVERNMENT?
— ♦️GALLOPING GAYE♦️ (@GallopingGaye) March 29, 2023
Take A Deep Breath
AND JUST LOOK AROUND!
Please Listen.
♦️♦️♦️♦️♦️
pic.twitter.com/0JKSAPMk8L
Organic Remediation and Toxic Cleanup Its Not Rocket Science - Its Phyto Science. The magic happens in the roots of the plants Naturally with Phytoremediation
Tuesday, March 21, 2023
We Went to East Palestine: What We Saw May Shock You
Thursday, March 16, 2023
Hemp plants can suck PFAS, aka "forever chemicals," out of the ground
Hemp, a variety of the plant Cannabis sativa, is often overshadowed by marijuana — a genetically distinct form of cannabis. Used for food, clothing, fuel, and plastics, it’s the seemingly more domestic member of the family.
However, new research suggests we should pay more attention to this nonpsychoactive substance. Hemp, scientists say, has an eco-friendly superpower: It can rid the environment of toxic chemicals.
Members of the Micmac (Mi'kmaq) Nation — a tribe indigenous to what’s now known as Canada’s eastern Maritime Provinces and parts of the northeastern United States — the activist group Upland Grassroots, and research scientists came together in 2019 to test methods for removing per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from land located at the Loring Air Force Base. After years of lobbying and dispute, portions of the former bomber base were given back to the Aroostook Band of Micmacs in 2018.
On Tuesday, the eclectic team published a commentary reflecting on their work and progress in the journal Cell Press. The project, so far, is a success: Results suggest planting small fields of fiber hemp removed a primary type of PFAS at the polluted site, a chemical called perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS).
“Protecting the land is part of the Micmac beliefs,” Chief E. Peter Paul of the Micmac Nation said in the commentary. “Anything we can do to contribute to making the environment better, we want to be a part of.”
What you need to know first — The idea of removing toxic contaminants from the soil by planting certain plants is known as “phytoremediation.”
Hemp is “versatile in extracting many different kinds of chemicals from the soil,” Chelli Stanley, a member of Upland Grassroots, states in the commentary.
Previous research has also demonstrated industrial hemp can be effective in phytoremediation.
“Hemp phytoremediation has been previously used for other types of soil contaminants – mainly metals,” Sara L. Nason, one of the lead researchers on the project, tells Inverse. Nason is a scientist affiliated with the Connecticut Agricultural Experiment station.
Friday, March 3, 2023
Mead Nebraska Ongoing Environmental Disaster
AltEn Crisis in Mead https://t.co/t2I33T6B1H NO ON CARES #OhioChemicalDisaster
— GHOST OF CHAOS (@GHOSTOFCHAOS420) March 3, 2023
I would like to appeal to the logical area of the brain for a moment. We know we're under attack by the state. Rather than expend our energy debating the precise nature of each tool being used to murder us, I suggest we focus our attention and talk about the only peaceful way out https://t.co/2I6l0V6h3h
— Roadtoserfdom (@roadtoserfdom3) March 3, 2023
Monday, February 27, 2023
Saturday, February 25, 2023
Microbe Bacteria DIOXIN Remediation
this was a @EPA and @DeptofDefense funded research project in Vietnam for Dioxin and Agent Orange remediation/soil reclamation. aka the EPA knows there are solutions avail to help in the #OhioChernobyl https://t.co/mMcCJWgnfg
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) February 26, 2023
Ohio Trainwreck Bioremediation Soil Treatment Research
JOINT STUDY OF BIOREMEDIATION AT PILOT SCALE FOR DETOXIFICATION OF HERBICIDE/DIOXIN IN DA NANG HOT SPOT, VIETNAM
Conclusions Aerobic bioremediation is capable of significantly reducing TCDD toxicity (p=0.0026). Bioaugmentation with small amounts of treated soil or contaminated sediment may be effective for anaerobic treatment. However, if suitable growth conditions are provided, the indigenous microbes in the mixed soil and sediment at Da Nang appear capable of degrading TCDD without adding another source of microbes. Anaerobic bioremediation rate is about half the rate of aerobic treatment, but the results are not as significant (p=0.25). From our of point active landfill containing both aerobic and anaerobic degradation become feasible resolution for detoxification of heavy herbicide/dioxin in full scale in Vietnam.
Bioremediation is recognized as a “Green Technology,” which has a very low energy requirement and produces few emissions. Bioremediation is a permanent solution which produces a soil which can be returned to beneficial use. Knowledge gained from this project by both Vietnamese and US scientists will allow for design of customized recipes suitable for addressing dioxin and other persistent organic pollution problems throughout Vietnam and elsewhere
@EPA Own Publications explained how to deal with #Ohio Chemical Incineration > U.S. Congress, Office of Technology Assessment, Dioxin Treatment Technologies Background Paper, OTA-BP-O-93 (Washington, DC: U.S. Government printing Office) pic.twitter.com/2VDdPloAYg
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) February 26, 2023
This type of Incinerator is very similar to the #Downdraft #Gasifer Offgrid Hot Water and Hot Air system I designed and shared months ago. https://t.co/Im01RKt8uo pic.twitter.com/jGsSxS4aor
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) February 26, 2023
#OhioChernobyl Research Files https://t.co/h1F8Khg5h6 to cleanup the #chemicals
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) February 26, 2023
This research paper from 1991 from the EPA CluIn Files for #Dioxin Incineration System provides a Diagram source file:
Dioxin Treatment Technologies
November 1991 OTA-BP-O-93 NTIS order PB92-152511 pic.twitter.com/VPsyW4ZqW1
Full-Scale Incineration System Demonstration
#Dioxin remediation research. #OhioChernobyl > Full-Scale Incineration System Demonstration 100 ton/day rotary kiln incinerator in processing soil contaminated with dioxins and other hazardous constituents of Herbicide Orange. https://t.co/upbFQtt2ha
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) February 26, 2023
@Elastec could the exhause heat generated by an inceneratior be used to spin a turbine of sorts to generate the electricity needed for a incenerator?
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) February 26, 2023
Full-Scale Incineration System Demonstration at the Naval Battalion Construction Center, Gulfport, Mississippi
Air Force Engineering and Services Center, ESL-TR-89-39, 1991
Cook, J.A., D.J. Haley, et al.
The overall goal of the project was to determine the cost and effectiveness of a 100 ton/day rotary kiln incinerator in processing soil contaminated with dioxins and other hazardous constituents of Herbicide Orange.
- Vol 1: Project Summary

- Vol 2: Part 1 - Contains the final report on the trial burns

- Vol 2: Part 2 - Contains Appendices A-H

- Vol 3: Treatability Tests, Part 1

- Vol 3: Treatability Tests, Part 2

- Vol 3: Treatability Tests, Part 3

- Vol 3: Treatability Tests, Part 4

- Vol 3: Treatability Tests, Part 5

- Vol 4: Incinerator Operations

- Vol 5: Incinerator Availability

- Vol 6: Soil Excavation

- Vol 7: Project Management/Site Services

- Vol 8: Delisting

- This research paper from 1991 from the EPA Clu-In Files for Dioxin Incineration System provides a Diagram source file:
- Dioxin Treatment Technologies
- November 1991
- OTA-BP-O-93
- NTIS order #PB92-152511 https://clu-in.org/download/contaminantfocus/dioxins/Dioxin-Treatment-Technologies-OTA-9116.pdf
.jpg) | |||||
| Dioxin Treatment Technologies | November 1991 | OTA-BP-O-93 | NTIS order #PB92-152511 | https://clu-in.org/download/contaminantfocus/dioxins/Dioxin-Treatment-Technologies-OTA-9116.pdf |
LIQUID INJECTION INCINERATION TECHNOLOGY Liquid injection (LI) is not currently available for dioxin treatment, but it has been used aboard ships for ocean-based incineration of Agent Orange. It is also employed in many industrial and manufacturing sectors for treatment of hazardous organic and inorganic wastes. As shown in figure 2-3, the typical LI incinerator consists of a burner, two combustion chambers (primary and secondary), a quench chamber, a scrubber, and a stack. Vertical LI incinerators are preferred for treating liquid waste rich in organics and salts (and therefore ash) because the incinerator unit can be used as its own stack to facilitate the handling of generated ash. Portions of the vertical LI unit can also be used as a secondary combustion chamber. The horizontally shaped LI units are connected to a tall stack and are preferred for treating liquid waste that generates less ash. In both systems, the use of external waste storage and blending tanks helps maintain the waste in a homogeneous form and at a steady flow.37 Some of the limitations that must be considered before applying LI incineration to dioxin destruction include the following: ● ● ● LI systems are applicable only to combustible low-viscosity liquids and slurries that can be pumped; waste must be atomized prior to injection into the combustor; and particle size is critical because burners are susceptible to clogging at the nozzles.3
@EPA Own Publications explained how to deal with #Ohio Chemical Incineration > U.S. Congress, Office of Technology Assessment, Dioxin Treatment Technologies Background Paper, OTA-BP-O-93 (Washington, DC: U.S. Government printing Office) pic.twitter.com/2VDdPloAYg
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) February 26, 2023
This type of Incinerator is very similar to the #Downdraft #Gasifer Offgrid Hot Water and Hot Air system I designed and shared months ago. https://t.co/Im01RKt8uo pic.twitter.com/jGsSxS4aor
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) February 26, 2023
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) February 26, 2023
Friday, February 24, 2023
Federal Remediation Technology Roundtable Technology Cost and Performance Reports
Federal Remediation Technology Roundtable Technology Cost and Performance Reports
- Glass Furnace Technology (GFT) Demonstration at the Hazen Research Center in Golden, Colorado and the Minergy GlassPack Test Center in Winneconne, Wisconsin (2004)
- In Situ Vitrification at the Parsons Chemical/ETM Enterprises Superfund Site, Grand Ledge, Michigan (1997)
- In Situ Vitrification, U.S. Department of Energy, Hanford Site, Richland, Washington; Oak Ridge National Laboratory WAG 7; and Various Commercial Sites (1997)
- Incineration at the Baird and McGuire Superfund Site, Holbrook, Massachusetts (1998) Incineration at the Times Beach Superfund Site, Times Beach, Missouri (1998)
- Incineration at the Vertac Chemical Corporation Superfund Site, Jacksonville, Arkansas (1998)
Research
Search This Blog
ElectroHemp Introduction
ElectroHemp Hazardous Waste Remediation Intro
ElectroHemp BioRad Hazardous Waste Cleanup Introduction ElectroHemp - BioRad CleanUp 5 Stage Phytoremediation Treatment Train - Remove...
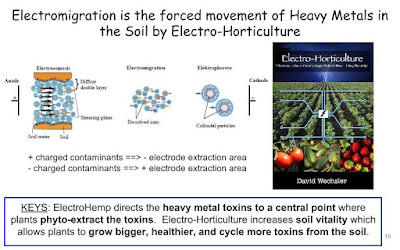
-
while reading this I realized the EPA are addressing the spread of the toxins but not the cause of the toxins. tsk tsk tsk @EPA Are you s...
-
ElectroHemp BioRad Hazardous Waste Cleanup Introduction ElectroHemp - BioRad CleanUp 5 Stage Phytoremediation Treatment Train - Remove...
-
If only more business cared about the environment as much as IKEA does. Most everyone has heard that the St Louis IKEA Store is powered ...




.jpg)



