Organic Remediation and Toxic Cleanup Its Not Rocket Science - Its Phyto Science. The magic happens in the roots of the plants Naturally with Phytoremediation
Wednesday, January 25, 2023
Westlake Landfill Testing Update
EPA Announces Latest Actions to Protect Groundwater and Communities from Coal Ash Contamination
Agency issues six proposed determinations to deny facilities’ requests to continue unsafe coal ash disposal Issued: Jan 25, 2023 (2:29pm EST)
WASHINGTON (Jan. 25, 2023) – Today, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced the latest action to protect communities and hold facilities accountable for controlling and cleaning up the contamination created by coal ash disposal. The Agency issued six proposed determinations to deny facilities’ requests to continue disposing of coal combustion residuals (CCR or coal ash) into unlined surface impoundments.
For a seventh facility that has withdrawn its application, Apache Generating Station in Cochise, Arizona, EPA issued a letter identifying concerns with deficiencies in its liner components and groundwater monitoring program.
“With today’s proposed denials, EPA is holding facilities accountable and protecting our precious water resources from harmful contamination, all while ensuring a reliable supply of electricity to our communities,” said EPA Administrator Michael S. Regan. “We remain committed to working with our state partners to protect everyone, especially those in communities overburdened by pollution, from coal ash contamination now and into the future.”
Coal ash is a byproduct of burning coal in coal-fired power plants that, without proper management, can pollute waterways, groundwater, drinking water, and the air. Coal ash contains contaminants like mercury, cadmium, chromium, and arsenic associated with cancer and various other serious health effects.
Today’s action delivers protections for underserved communities already overburdened by pollution, and reflects the Biden-Harris Administration’s commitment to advancing environmental justice in impacted communities.
EPA is proposing to deny the applications for continued use of unlined surface impoundments at the following six facilities:
- Belle River Power Plant, China Township, Michigan.
- Coal Creek Station, Underwood, North Dakota.
- Conemaugh Generating Station, New Florence, Pennsylvania.
- Coronado Generating Station, St. Johns, Arizona.
- Martin Lake Steam Electric Station, Tatum, Texas.
- Monroe Power Plant, Monroe, Michigan.
EPA is proposing to deny these applications because the owners and operators of the CCR units fail to demonstrate that the surface impoundments comply with requirements of the CCR regulations. Specifically, EPA is proposing to deny these applications due to:
- Inadequate groundwater monitoring networks.
- Failure to prove groundwater is monitored to detect and characterize any elevated levels of contaminants coming from the coal ash surface impoundment.
- Evidence of potential releases from the impoundments and insufficient information to support claims that the contamination is from sources other than the impoundments.
- Inadequate documentation for the design and performance of the impoundment liners.
- Failure to meet all location restrictions.
If EPA finalizes these denials, the facilities will have to either stop sending waste to these unlined impoundments or submit applications to EPA for extensions to the deadline for unlined coal ash surface impoundments to stop receiving waste.
In the significant interest of maintaining grid reliability, the Agency is also proposing a process for these facilities to seek additional time, if needed to address demonstrated grid reliability issues. This process relies in part on reliability assessments from the relevant regional transmission organizations, ensuring a reliable supply of electricity while protecting public health.
EPA is collecting public comments on these proposals for 30 days through dockets in Regulations.gov. For more information, visit the Part B implementation webpage.
Background
The CCR Part B Final Rule, published November 12, 2020, allowed facilities to demonstrate to EPA that, based on groundwater data and the design of a particular surface impoundment, the operation of the unit has and will continue to ensure there is no reasonable probability of adverse effects to human health and the environment. EPA approval would allow the unit to continue to operate.
EPA received applications for alternate liner demonstrations from eight facilities with 17 CCR surface impoundments. These applications were from facilities in Arizona, Louisiana, Michigan, North Dakota, Pennsylvania, and Texas. One Arizona facility and the Louisiana facility have since withdrawn their applications.
Learn more about coal ash
Wednesday, January 18, 2023
Italian researcher says hemp stalks from polluted soil OK for building, energy
The efficiency of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) in remediating sites
Conclusions
It was demonstrated that hemp accumulates copper, chromium, nickel, and zinc preferentially in the leaves, while lead is distributed mainly in the stems of the plant. Such selective compartmentalization is enhanced when the plant is irrigated with water containing spirulina. It was found that, at higher concentrations, spirulina acts as a growth promoter, contributing to an increase in the final generated biomass. Also, it was demonstrated that the treatment with spirulina during the cultivation of the hemp induced an enhancement in the uptake of heavy metals, except for lead. Such a result may be explained by assuming a strong affinity of spirulina towards the lead, resulting in confinement of this metal inside the soil and hampering its uptake by the plant. The NMR analysis allowed to identify the crucial variations of the metabolic composition that were induced by the treatment with spirulina. Results reported in this work pave the way to further studies aimed to understand the optimal dose of spirulina to enhance the efficiency of this innovative combined remediation bio-system. Furthermore, the results described may encourage the application of spectroscopic methods for the rapid detection of structural changes in the various environmental spheres, allowing prompt intervention through the adoption of remediation schemes
Monday, January 16, 2023
Electricity Production by Geobacter sulfurreducens Attachedto Electrodes
here is the science behind the Electrohemp Pollution Disposal Energy Fuel Cell:
Thursday, November 24, 2022
yet another natural remedy
here is yet another example: nature has a cure for what ails mankind! thank you for sharing.
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) November 24, 2022
"... other proteins also worked, so it may be possible to utilize those as to not strain the {egg} market as much. An even bigger concern is water purification [removes salt] ... " https://t.co/CULB5BwJz9
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) November 24, 2022
So if plants remove toxins its called Phytoremediation.
What will be the term invented for when Eggs or Proteins remove toxins? - egremediation or proremediation
So if plants remove toxins its called #Phytoremediation.
— systembuster (@stlsystembuster) November 24, 2022
What will be the term #invented for when Eggs or Proteins remove toxins? #Poll
Search This Blog
ElectroHemp Introduction
ElectroHemp Hazardous Waste Remediation Intro
ElectroHemp BioRad Hazardous Waste Cleanup Introduction ElectroHemp - BioRad CleanUp 5 Stage Phytoremediation Treatment Train - Remove...
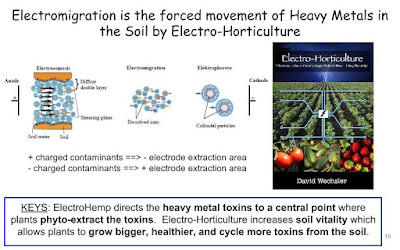
-
while reading this I realized the EPA are addressing the spread of the toxins but not the cause of the toxins. tsk tsk tsk @EPA Are you s...
-
If only more business cared about the environment as much as IKEA does. Most everyone has heard that the St Louis IKEA Store is powered ...
-
ElectroHemp BioRad Hazardous Waste Cleanup Introduction ElectroHemp - BioRad CleanUp 5 Stage Phytoremediation Treatment Train - Remove...




.jpeg)



