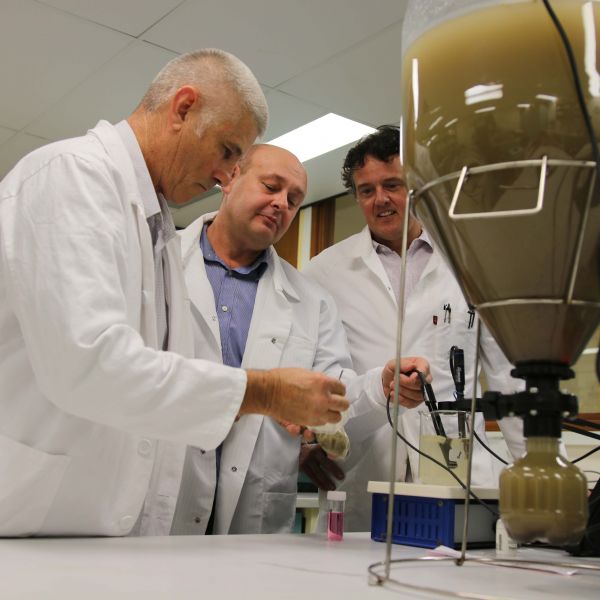
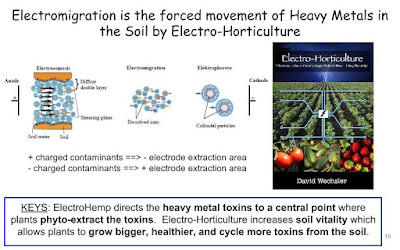
The EPA has previously listed about 194 ongoing Phytoremediation / bioremediation field research projects. Yr 2000
| 194 ongoing phytoremediation field research projects, EPA |
Heavy metals and radionuclides represent about 30% of this activity supporting that bioremediation is a feasible technology to decontaminate the environment.Unlike many organic contaminants most:
- metals and radionuclides cannot be eliminated from the environment by chemical or biological transformation.
- Although it may be possible to reduce the toxicity of certain metals by influencing their speciation,
- they do not degrade and are persistent in the environment.
The conventional remediation technologies that are used to clean heavy metal polluted environments are:
- soil in situ vitrification
- soil incineration
- excavation and landfill
- soil washing
- soil flushing
- solidification
- stabilization with electrokinetic systems
| Source: Electronic Journal of Biotechnology |