Organic Remediation and Toxic Cleanup Its Not Rocket Science - Its Phyto Science. The magic happens in the roots of the plants Naturally with Phytoremediation
Wednesday, December 9, 2020
Saturday, September 26, 2020
Kenaf Hibiscus Cannabinus L for Phytoremediation -Science Studies-
- Phytoextraction of As and Fe using Hibiscus cannabinus L. from soil polluted with landfill leachate.Meera M, Agamuthu P.Int J Phytoremediation. 2012 Feb;14(2):186-99. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2011.587481.PMID: 22567704
- Effects of peat on plant growth and lead and zinc phytostabilization from lead-zinc mine tailing in southern China: Screening plant species resisting and accumulating metals.Tang C, Chen Y, Zhang Q, Li J, Zhang F, Liu Z.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019 Jul 30;176:42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.078. Epub 2019 Mar 25.PMID: 30921695
- Potential of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) and corn (Zea mays L.) for phytoremediation of dredging sludge contaminated by trace metals.Arbaoui S, Evlard A, Mhamdi Mel W, Campanella B, Paul R, Bettaieb T.Biodegradation. 2013 Jul;24(4):563-7. doi: 10.1007/s10532-013-9626-5. Epub 2013 Feb 23.PMID: 23436151
- Ascorbate-Glutathione Cycle and Ultrastructural Analyses of Two Kenaf Cultivars (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) under Chromium Stress.Niu L, Cao R, Kang J, Zhang X, Lv J.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Jul 11;15(7):1467. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15071467.PMID: 29997377 Free PMC article.
- Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) Seed and its Potential Food Applications: A Review.Giwa Ibrahim S, Karim R, Saari N, Wan Abdullah WZ, Zawawi N, Ab Razak AF, Hamim NA, Umar RA.J Food Sci. 2019 Aug;84(8):2015-2023. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14714. Epub 2019 Jul 30.PMID: 31364175 Review.
- [Using kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) to reclaim multi-metal contaminated acidic soil].Yang YX, Lu HL, Zhan SS, Deng TH, Lin QQ, Wang SZ, Yang XH, Qiu RL.Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2013 Mar;24(3):832-8.PMID: 23755502 Chinese.
- Nitrogen dioxide at an ambient level improves the capability of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) to decontaminate cadmium.Takahashi M, Adam SE, Konaka D, Morikawa H.Int J Phytoremediation. 2008 Jan-Feb;10(1):73-6. doi: 10.1080/15226510701827085.PMID: 18709933
- Phytotreatment of soil contaminated with used lubricating oil using Hibiscus cannabinus.Abioye OP, Agamuthu P, Abdul Aziz AR.Biodegradation. 2012 Apr;23(2):277-86. doi: 10.1007/s10532-011-9506-9. Epub 2011 Aug 26.PMID: 21870160
- Potential of Sonchus arvensis for the phytoremediation of lead-contaminated soil.Surat W, Kruatrachue M, Pokethitiyook P, Tanhan P, Samranwanich T.Int J Phytoremediation. 2008 Jul-Aug;10:325-42. doi: 10.1080/15226510802096184.PMID: 19260217
- Physiological responses and tolerance of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) exposed to chromium.Ding H, Wang G, Lou L, Lv J.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2016 Nov;133:509-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.08.007. Epub 2016 Aug 21.PMID: 27553521
- Morpho-physiological traits, biochemical response and phytoextraction potential of short-term copper stress on kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) seedlings.Saleem MH, Fahad S, Rehman M, Saud S, Jamal Y, Khan S, Liu L.PeerJ. 2020 Jan 30;8:e8321. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8321. eCollection 2020.PMID: 32030320 Free PMC article.
- Phytoremediation of lead (Pb) and arsenic (As) by Melastoma malabathricum L. from contaminated soil in separate exposure.Selamat SN, Abdullah SR, Idris M.Int J Phytoremediation. 2014;16(7-12):694-703. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2013.856843.PMID: 24933879
- Growth and lead accumulation by the grasses Vetiveria zizanioides and Thysanolaena maxima in lead-contaminated soil amended with pig manure and fertilizer: a glasshouse study.Rotkittikhun P, Chaiyarat R, Kruatrachue M, Pokethitiyook P, Baker AJ.Chemosphere. 2007 Jan;66(1):45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.05.038. Epub 2006 Jul 10.PMID: 16828842
- Phytostabilization of a Pb-contaminated mine tailing by various tree species in pot and field trial experiments.Meeinkuirt W, Pokethitiyook P, Kruatrachue M, Tanhan P, Chaiyarat R.Int J Phytoremediation. 2012 Oct;14(9):925-38. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2011.636403.PMID: 22908655
- Role of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on lead uptake and translocation by tumbleweed (salsola kali L.).de la Rosa G, Peralta-Videa JR, Cruz-Jimenez G, Duarte-Gardea M, Martinez-Martinez A, Cano-Aguilera I, Sharma NC, Sahi SV, Gardea-Torresdey JL.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2007 May;26(5):1033-9. doi: 10.1897/06-239r.1.PMID: 17521152
- Bioremediation of industrially contaminated soil using compost and plant technology.Taiwo AM, Gbadebo AM, Oyedepo JA, Ojekunle ZO, Alo OM, Oyeniran AA, Onalaja OJ, Ogunjimi D, Taiwo OT.J Hazard Mater. 2016 Mar 5;304:166-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.10.061. Epub 2015 Oct 30.PMID: 26551220
- Effect of Emulsification Method and Particle Size on the Rate of in vivo Oral Bioavailability of Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) Seed Oil.Cheong AM, Tan CP, Nyam KL.J Food Sci. 2018 Jul;83(7):1964-1969. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14191. Epub 2018 May 26.PMID: 29802733
- Phytoremediation of wastewater containing lead (Pb) in pilot reed bed using Scirpus grossus.Tangahu BV, Abdullah SR, Basri H, Idris M, Anuar N, Mukhlisin M.Int J Phytoremediation. 2013;15(7):663-76. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2012.723069.PMID: 23819266
- Phytoextraction of Pb and Cd by the Mediterranean saltbush (Atriplex halimus L.): metal uptake in relation to salinity.Manousaki E, Kalogerakis N.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2009 Nov;16(7):844-54. doi: 10.1007/s11356-009-0224-3. Epub 2009 Jul 14.PMID: 19597858
- Lead accumulation, growth responses and biochemical changes of three plant species exposed to soil amended with different concentrations of lead nitrate.Chandrasekhar C, Ray JG.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019 Apr 30;171:26-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.058. Epub 2018 Dec 27.PMID: 30594754
Saturday, July 4, 2020
Tuesday, May 7, 2019
Friday, April 26, 2019
Trees Shrubs as Farm Buffer Zones
Trees and Shrubs growing along the edge of fields act as Farm Buffer Zones and clean farm runoff which protect streams and waterways from toxins and pollutants
RIPARIAN FOREST BUFFERS are trees, shrubs, and grasses located next to rivers, streams, and lakes to help protect aquatic resources by filtering farm runoff and preventing erosion. Buffer areas can support wildlife habitat, produce crops, improve water quality, and reduce flood damage.

Riparian forest buffers are natural or re-established streamside forests made up of tree, shrub, and grass plantings. They buffer non-point source pollution of waterways from adjacent land, reduce bank erosion, protect aquatic environments, enhance wildlife, and increase biodiversity.USDA
Tools
- Conservation Buffers: Design Guidelines for Buffers, Corridors, and Greenways
- Buffer$
- AgBufferBuilder: A Filter Strip Design Tool for GIS
- Riparian Bibliography (Vegetated Stream Riparian Zones: Their Effects on Stream Nutrients, Sediments, and Toxic Substances)
Tuesday, April 16, 2019
Funding Available for Water-Quality Stations that Measure Effectiveness of Conservation Systems on Farms
The USDA’s Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) is making $2 million available to interested farmers to help install voluntary edge-of-field monitoring stations on agricultural land in five states, including Missouri. COLUMBIA, MO, April 16, 2019 –

“Edge-of-field water quality monitoring provides quantifiable data that supports voluntary-based conservation efforts aimed at reducing the movement of sediment and nutrients off Missouri farms,” State Conservationist J.R. Flores said.
Through edge-of-field monitoring, NRCS works with farmers and conservation partners, such as universities and non-governmental organizations, to monitor the amount of nutrients and sediment in water runoff from a field. The data from different conservation systems, and from field with no conservation systems in place, are evaluated to judge effectiveness of the systems. Conservation practices typically evaluated include cover crops, no till, irrigation water management, and practices to reduce and trap nutrients and sediment.
Monitoring stations enable NRCS to measure at the edge of farm fields rather than try to estimate conservation effects from in-stream measurements that are subject to influences outside of the farmer’s control. Edge-of-field monitoring, combined with instream monitoring, can provide a more thorough picture of improvements within a watershed.
NRCS first introduced edge-of-field monitoring in 2011. Since then 19 stations have been in operation in Missouri. Generally, they have shown that conservation practices work best when they are part of an overall system. They also show the importance of having live plants growing during the winter. Flores said the stations have been showing that winter cash crops or cover crops reduce pollutant loading up to 30 percent.
Funding is available on a voluntary basis to farmers in 116 Missouri watersheds. It pays for the costs of installing, maintaining and monitoring the stations for up to nine years. Farmers can check with the NRCS office in their county to see if they are eligible. The results of data collected will be maintained confidentially for farmers’ use and for use by the conservation partners responsible for monitoring.
Farmers interested in applying for financial assistance should submit applications by July 15 to their local NRCS office. To locate an NRCS service center near you, visit the “contact us” section of the website, or look in the telephone directory under, “U.S. Government, Department of Agriculture.”
|
Sunday, April 7, 2019
ElectroHemp is on Ideascale looking for Partners
https://mohempenergy.ideascale.com/a/ideas/top/campaigns/16398
__________
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Search This Blog
ElectroHemp Introduction
ElectroHemp Hazardous Waste Remediation Intro
ElectroHemp BioRad Hazardous Waste Cleanup Introduction ElectroHemp - BioRad CleanUp 5 Stage Phytoremediation Treatment Train - Remove...
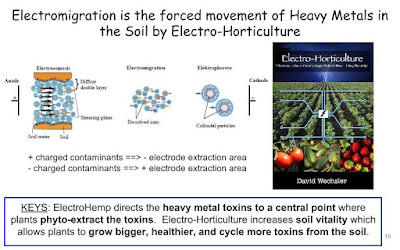
-
while reading this I realized the EPA are addressing the spread of the toxins but not the cause of the toxins. tsk tsk tsk @EPA Are you s...
-
ElectroHemp BioRad Hazardous Waste Cleanup Introduction ElectroHemp - BioRad CleanUp 5 Stage Phytoremediation Treatment Train - Remove...
-
If only more business cared about the environment as much as IKEA does. Most everyone has heard that the St Louis IKEA Store is powered ...







